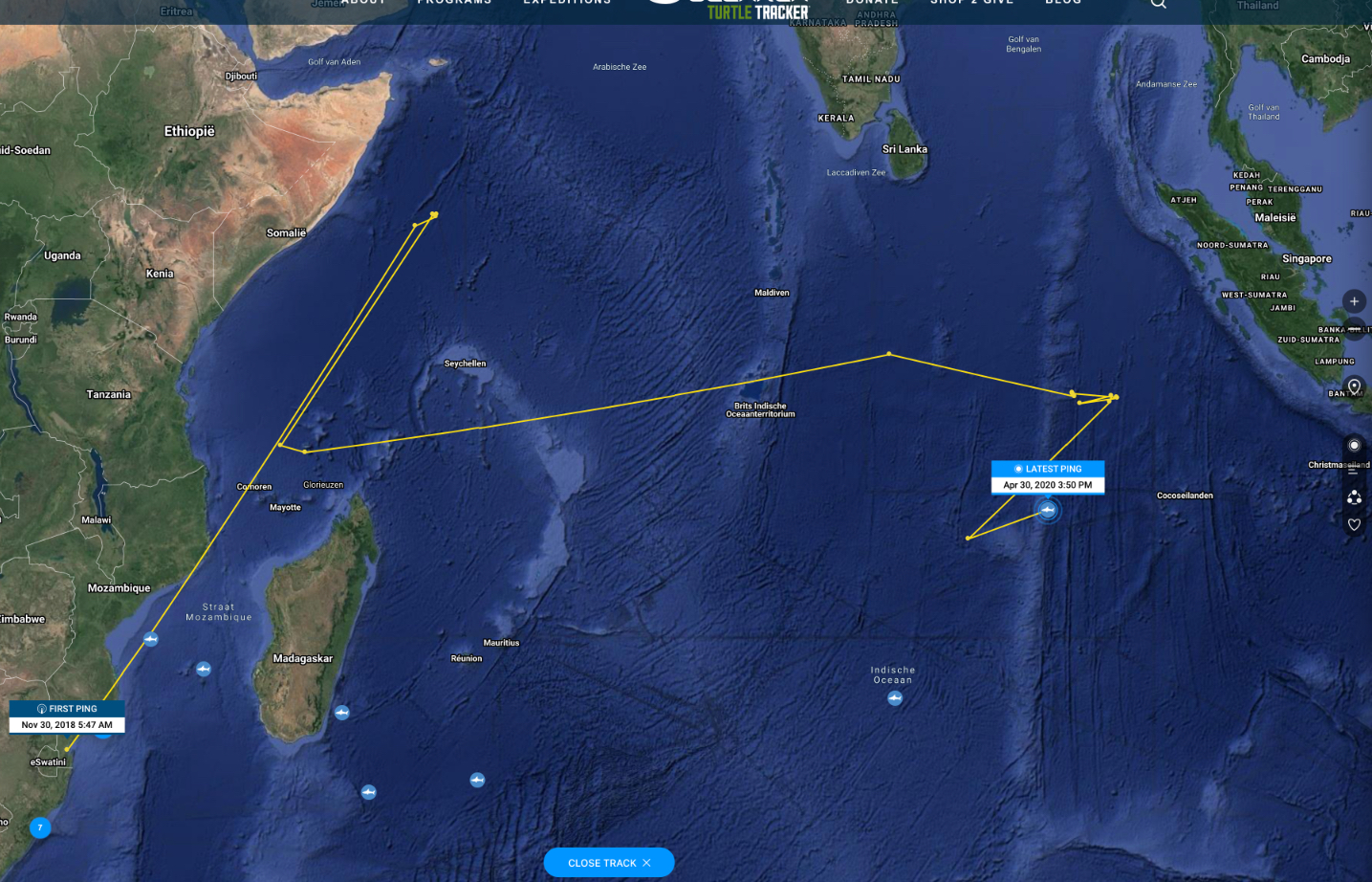
PARK CITY (USA)- Tiger sharks are usually found close to coasts in tropical and subtropical waters. But now research confirmed that tiger sharks are also long distance travellers. Collaborating scientists at Biopixel Oceans Foundation and the Oceanographic Research Institute used the OCEARCH Tracker to follow a tagged 10-foot-4-inch mature female tiger shark, named Sereia. She was tagged on the African coast in Mozambique in November 2018 and was detected via satellite in April 2020 about 800 miles off the Indonesian coast, a transoceanic journey of more than 4,000 miles. Sereia now has the longest confirmed migration for the species on record.
“We had no idea a shark from Mozambique would end up off the coast of Indonesia,” said Dr Ryan Daly of the Oceanographic Research Institute in Durban South Africa in a press release. Dr. Daly is also a research associate at the South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity. “This is incredibly important because it confirms that tiger sharks are roaming throughout the Indian Ocean and we need to take this into account when thinking about improving conservation for them in the region,” he adds.
Tiger sharks
Sereia is one of 21 sharks tagged by Biopixel Oceans Foundation and the Oceanographic Research Institute in Mozambique as part of a project to lay down a baseline understanding of tiger shark movements and habitat use in the West Indian Ocean. Prior to starting the project, very little was known about the residency patterns and migration dynamics of tiger sharks in this region. The tags for Sereia and other tiger sharks in the project were deployed in the Ponta do Ouro Partial Marine Reserve which neighbours South Africa. Researchers hope that by studying the trans boundary movements of tiger sharks in this area that it will help in implementing congruent management plans on both sides of the border.
Sereia’s groundbreaking journey also sheds light on another important question the study aims to answer regarding the range tiger sharks are capable of covering. Prior to Sereia’s journey, most of the other sharks tagged in the study remained close to the African coast, with a couple venturing as far as Madagascar. Sereia’s most recent detection at the end of April show’s she may have turned around, but the magnitude of her migration still opens up a whole new line of questioning.
Follow Sereia on the OCEARCH Tracker?
Research
The research by Biopixel Oceans Foundation and the Oceanographic Research Institute also received funding from Save Our Seas Foundation along with National Geographic and the Guy Harvey Institute. The data was shared with OCEARCH so that it could be displayed on the Tracker. These organizations share OCEARCH’s philosophy about opening up the data to share with the public so that it can be used to engage communities across the world and unite them in our mission to ensure healthy oceans for future generations.
Read more on the research on Globe News Wire.
More on OCEARCH.